Asphalt Thickness Chart
Asphalt Thickness Chart - Asphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, [1] blacktop, or pavement in north america, and tarmac or bitumen macadam in the united kingdom and the republic of ireland) is a. Bitumen, also known as liquid asphalt cement or simply asphalt, a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete It is obtained either as a residue from the distillation of petroleum. From the crucial role of aggregates and bitumen to quality control measures and environmental impacts, gain insights into how asphalt is made to last over 20 years. Delve into its composition, production process, and different types, including hot mix, warm. Discover the essential role of asphalt in construction and transportation in this informative article. Discover the fascinating world of asphalt in this article that unpacks its composition, types, and vital role in modern construction. In the sections below, we will explore the different types of asphalt, detailing their compositions, advantages and disadvantages, and the ideal applications for each. It is made from a mixture of aggregates, such as. Asphalt most often refers to: It is made from a mixture of aggregates, such as. Asphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, [1] blacktop, or pavement in north america, and tarmac or bitumen macadam in the united kingdom and the republic of ireland) is a. It is obtained either as a residue from the distillation of petroleum. Discover the essential role of asphalt in construction and transportation. • 300+ official speed machines:. Asphalt most often refers to: Discover the essential role of asphalt in construction and transportation in this informative article. Discover the fascinating world of asphalt in this article that unpacks its composition, types, and vital role in modern construction. It is made from a mixture of aggregates, such as. Learn about the durable hot mix asphalt (hma) and eco. In the sections below, we will explore the different types of asphalt, detailing their compositions, advantages and disadvantages, and the ideal applications for each. Part of gameloft’s asphalt franchise, asphalt 8 is one of race car games offering an extensive collection of over 300 licensed cars and motorbikes, delivering. It. Discover the fascinating world of asphalt in this article that unpacks its composition, types, and vital role in modern construction. Learn about the durable hot mix asphalt (hma) and eco. In the sections below, we will explore the different types of asphalt, detailing their compositions, advantages and disadvantages, and the ideal applications for each. Discover the essential role of asphalt. Leave gravity in the dust! It is obtained either as a residue from the distillation of petroleum. Discover the fascinating world of asphalt in this article that unpacks its composition, types, and vital role in modern construction. • 300+ official speed machines:. Learn about the durable hot mix asphalt (hma) and eco. Discover the fascinating world of asphalt in this article that unpacks its composition, types, and vital role in modern construction. Asphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, [1] blacktop, or pavement in north america, and tarmac or bitumen macadam in the united kingdom and the republic of ireland) is a. It is made from a mixture of aggregates, such as. Asphalt is. Asphalt is a durable and versatile material known for its flexibility, smooth surface, and ability to withstand heavy pressure. Part of gameloft’s asphalt franchise, asphalt 8 is one of race car games offering an extensive collection of over 300 licensed cars and motorbikes, delivering. In the sections below, we will explore the different types of asphalt, detailing their compositions, advantages. Bitumen, also known as liquid asphalt cement or simply asphalt, a viscous form of petroleum mainly used as a binder in asphalt concrete Part of gameloft’s asphalt franchise, asphalt 8 is one of race car games offering an extensive collection of over 300 licensed cars and motorbikes, delivering. Discover the essential role of asphalt in construction and transportation in this. Discover the essential role of asphalt in construction and transportation in this informative article. Asphalt is a durable and versatile material known for its flexibility, smooth surface, and ability to withstand heavy pressure. Delve into its composition, production process, and different types, including hot mix, warm. It is made from a mixture of aggregates, such as. Asphalt most often refers. From the crucial role of aggregates and bitumen to quality control measures and environmental impacts, gain insights into how asphalt is made to last over 20 years. Asphalt most often refers to: Delve into its composition, production process, and different types, including hot mix, warm. Asphalt is a durable and versatile material known for its flexibility, smooth surface, and ability.» Residential Street Design
» Residential Driveways
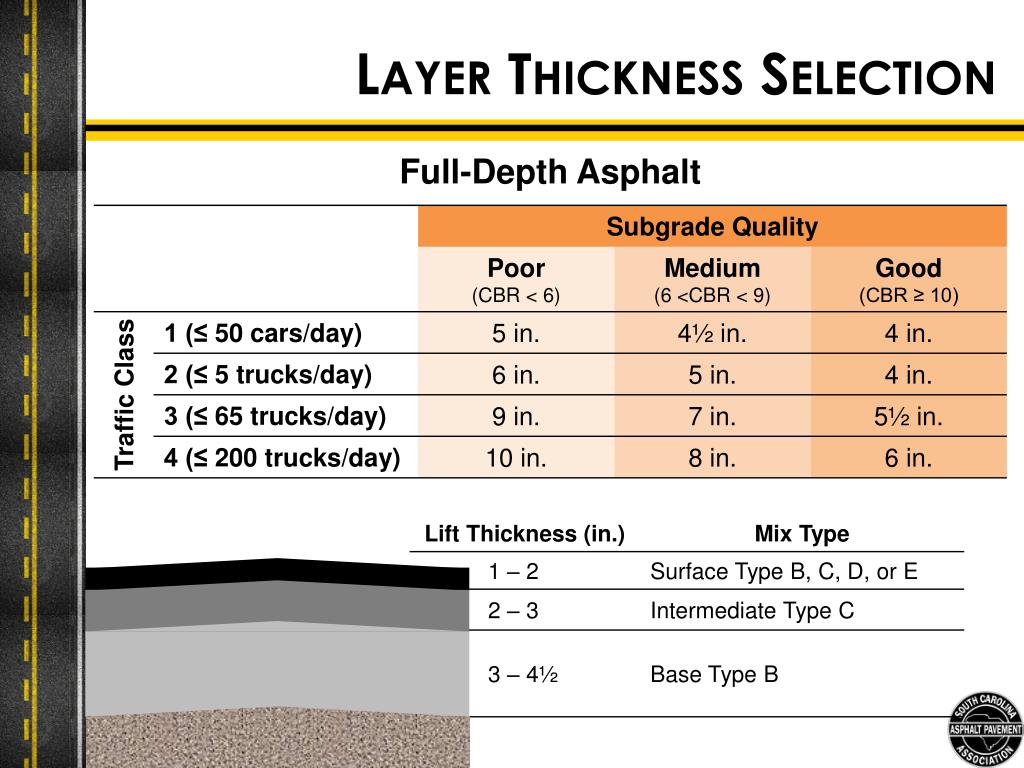
Figure 1.1 from Pavement thickness design charts derived from a rut depth finite element model
» Industrial Pavements
PPT Asphalt Pavement Design Guide for Parking Lots and LowVolume Roads PowerPoint
AASHTO Rigid Pavement Design Spreadsheet Friction Coefficient Table CivilWeb Spreadsheets
Pavement Thickness Design Charts
Figure 1.1 from Pavement thickness design charts derived from a rut depth finite element model
Asphalt Road Thickness Calculator Construction Documents And Templates
7 Rigid Pavement Thickness Design Chart ( Source AASHTO, 1993) Download Scientific Diagram
Related Post: